Army takes lead in promoting India's green hydrogen mission

The Indian army has taken the lead in promoting India’s green hydrogen mission by exploring various options for producing green hydrogen. India has set a goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070, and green hydrogen is expected to play a critical role in achieving this objective.
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, and it can be used as a clean alternative to fossil fuels in various sectors such as transportation, power generation, and manufacturing.

Green Hydrogen Mission in Army
One of the Army’s main initiatives is to develop green hydrogen-powered vehicles for military use. The army is working with several Indian companies to develop hydrogen fuel cell-powered tanks, trucks, and other vehicles. the army has already conducted successful tests of hydrogen fuel cell-powered vehicles and is working to scale up production.
The Army’s efforts to promote the use of green hydrogen in military vehicles are significant because the Army is one of the largest consumers of energy in India. by promoting the use of green hydrogen in military vehicles, the Army is not only reducing its own carbon footprint but is also contributing to India’s efforts to achieve its net-zero carbon emissions goal.

The Army’s partnerships with Indian companies have led to the development of new technologies and products that can be used in the production and use of green hydrogen. Another area where the Army is promoting the use of green hydrogen is in power generation.
The Army has set up a green hydrogen plant at its base in Leh, Ladakh, Which is powered by a 1.5 MW solar power plant. The plant can produce up to 1.7 kg of hydrogen per hour, which will be used to power produce hydrogen, and the army plans to use the hydrogen to power generators and other equipment.
India has set an ambitious target of 450GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, and green hydrogen is expected to play a key role in achieving this goal. The country has significant renewable energy potential, particularly in solar and wind power, and the production of green hydrogen could help to harness this potential while reducing the country’s dependence on fossil fuels.
In addition to initiatives, the army is also promoting the use of green hydrogen in civilian applications. The Army has partnered with the Indian oil corporation to develop green hydrogen refuelling stations for civilian vehicles. The Army is also working with other government agencies and private companies to promote the use of green hydrogen in various sectors.
Overall, the Army’s efforts to promote India’s green hydrogen mission are an excellent example of how government agencies can lead by example in promoting clean energy. The Army’s initiative has helped to create new opportunities for Indian companies in the green hydrogen sector.
They are contributing to India’s efforts to achieve its net-zero carbon emissions goal. As India continues to focus on achieving its clean energy objectives, it is likely that the Army’s efforts will serve as a model for other government agencies and private companies to follow.
Indian Army has announced a plan to set up a pilot project to produce green hydrogen at the Leh-based Siachen brigade, located at an altitude of 12,000 feet. The project will be implemented in collaboration with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
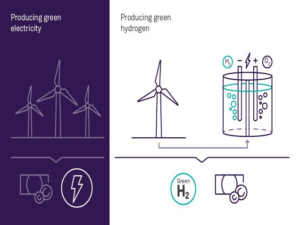
The production of green hydrogen is a critical component of India’s strategy to transition to a low-carbon economy. Green hydrogen is produced by electrolyzing water using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power.
The process generates zero carbon emissions and the resulting hydrogen can be used as a fuel for vehicles, power plants and other applications. The Indian government has also announced plans to launch a National Hydrogen Energy Emission to promote the production and use of hydrogen in the country. The mission will focus on developing a hydrogen economy, Which will include the production, storage, and transportation of hydrogen
In conclusion, the Indian Army’s pilot project to produce green hydrogen is a significant step in promoting India’s green hydrogen mission. The project will demonstrate the feasibility of using green hydrogen in high-altitude regions and is expected to play a crucial role in achieving India’s target of producing 450 GW of renewable energy by 2030.







