CRIMES BY MINORS ARE ON THE RISE

Children are the foundation of human society. The shape of the future of human society shall be determined by their mental and physical well-being.
Specific care needs to be taken that children grow up to become agile citizens, physically fit, mentally sound alert and socially and morally healthy but unfortunately, in spite of there being a number of resolutions and laws both at national and global levels, the conditions of children is far from satisfactory.
The Indian Penal Code and the various protective and preventive “special and local laws” specifically mention the offences wherein children are victims. Protection of children from crimes is the collective responsibility of the state, family and society.

Rise and reasons– Recently, there has been an increase in the crime rate among minors and among youngsters under the age of 18 years and the 21st century is witnessing it all worse. The surge of criminal offences including physical, cybercrime, and social are increasing at an alarming rate.
The basic psychology behind this is that they do not get sufficient emotional and social learning from parents and teachers. Today’s modern lifestyle is keeping parents occupied in earning and children are more addicted to computer games, surfing the net and social media. These video games are believed to encounter a number of crimes and are blamed for school shootings, serious crimes, sexist acts of violence and criminal behaviour.
A few of the mastermind virtual games that made crime a cup of tea for juveniles are- Cinnamon Challenge, Blue Whale, Fire Fairy, Five Finger Fillet, The Cutting Challenge and so many that put up daring tasks where not only the juvenile committed a crime and harmed others but risked and ended their priceless life too. Such games not only become the addiction of those brainwashed and manipulated children but also become a desperate means of survival, making them aggressive.
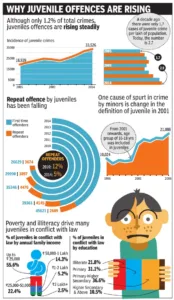
Not only ending here but there are also other factors like poverty that influence the basic social-economical life, domestic violence during childhood, friends and companions and drug abuse that helped in the rise of crimes by minors.
Whether exposed or not to the brutal images, one starving would steal a piece of bread. Such socio-economical factors can lead to such actions that make breaking the laws easier than surviving reality.
Cybercrimes are so common and trending among minors due to the use of the cyber world, addiction to social media, online games and the dares they challenge to do and the negative roles of the movies are arguable.
Due to the lack of moral and ethical values from the parents and teachers, juvenile delinquents are increasing at a mammoth rate and are increasing suicidal tendencies too. There are some psychological reasons like mental illness, personality traits and individualised emotional issues that can result in heinous crimes.
Indian authorities charged 27936 minors in the year 2012 for involvement in crimes like banditry, murder, rape and rioting. According to National Crime Records Bureau reports, child offenders appearing before the Juvenile Justice Board were mainly teenagers between the ages of 16 and 18. 72% of petty crimes such as stealing, burglary and inflicting harm are committed by juveniles. In 2021, 31170 cases of juveniles were registered all across the country drawing a 4.7% increase in crime rate over 2020.
Legal perspective-. In the eye of the law, a child who is below the age of 7 years is called ‘doli incapax’ which means that the child lacks or is incapable to understand the nature of the crime or its consequences thereby forming mens rea.
A child above 7 years and below 12 years of age would be held liable for an offence if he/she possesses the ability to understand the crime and its consequences. A child between the age of 16 to 18 years would be held liable for the heinous crime committed proved and provided that he/ she was able to understand the nature and consequence of the crime.

To deal with the offences committed by juveniles, there are so many legal provisions mentioned in the Indian Penal Code, Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2000 and under this act such children are defined as ‘children in conflict with law’.
Juvenile crime cases in India- few cases are as mentioned:
- On December 16th, 2012 on a moving bus in South Delhi a girl was abducted, raped and killed. The offenders of this horrific crime were a juvenile and his companions.
- On November 29, 2013; a group of 5 children escaped the city juvenile home at Mayur Vihar amid riot and violence. They eloped with 50 kg silver jewellery and Rs. 10 lakhs cash after murdering a jeweller’s wife.
- On February 24th, 2016 a 17 years old boy strangled an elderly woman in Delhi after being released from a Juvenile home for good behaviour.
- 2 juveniles on April 6th 2016 shot an Uber driver in the Mundka area, dumped his body and fled with the car.
- On December 22, 2017, a 22 years old woman has allegedly of her raped by 5 men out of which 4 were juveniles.
Evil effects – juvenile crimes do not only hamper the family and society but also the very child’s life at large. Such a child may lose their freedom after being placed on probation or incarcerated. This would end up affecting its academic development, and welfare and result in more school dropouts. Such a child may undergo unpredictable psychological damage and hamper the basic rights of a child.

Juvenile crime is a grim reality and the upward trend of juvenile crimes has become a global concern. The criminal responsibility of minors should be treated differently than adults and must be handled more carefully as they are more vulnerable.
The government is taking the initiatives necessary to deal with these issues such as keeping a check on available online games, outlaw of pornography and vulgar movies for minors, and providing child guidance centres and training centres in the districts.
The government is also working in collaboration with NGOs, educational institutes, legal bodies and law enforcement, courts and social workers.
Not only the government, we parents and the citizens will need to take measures to minimize the crimes committed by the child and ensure them a better living and the enjoyment of the basic rights they are entitled to rather than leaving them in their own state walking on the wrong path.







