IMPACT OF COVID-19 IN INDIA: AN AWFUL HISTORY STILL IN THE MAKING
ABSTRACT
“If we need to really unravel the problem, we need to collaborate, create collectives, and take solutions at scale”-Ravi Venkatesan
The intervention of virus or flu is nothing new to the world, it had left unprecedented famine or disaster wherever spread. History says whenever people have tried to play with the nature; it has retaliated in its worst form. Till they realize its adverse effect, things go out of control and curse the human civilisation making it hell to survive resulting breathless days and nights. Unfortunately, the truth of any human being is that, until things go above head it is taken lightly and presumed to be non-perpetual. It’s high time when people must realize that we all should stand with the principle of “Vasudev Kutumbakam” that means that the whole world is one single family. It is a time for international unity, not playing politics with public health. As it has become unambiguous that WHO (World Health Organization) has affirmed COVID-19 to be a pandemic. More than 200 nations are making out to contain the multiplicity of the disease and consequent human life losses with social distancing by way of lockdowns. Our nation has developed a common consensus to combat the pandemic with unbeatable measures keeping concern with global approaches and guidelines from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and the Ministry of Home Affairs. In the unifying fortitude of involvement, the Government is appealing with all citizens to battle the virus. The country’s infrastructure is united to support all containment methods while ensuring safety and sustenance of lives of all social strata. Policy, plans and announcements from stakeholders in all essential sectors such as Railways, Civil Aviation, Transport and Finance specify the vigilance to collaboratively combat the pandemic. This article focuses on the impact of COVID-19 on Society and International relationship. Where everyone is on the same table of death and can only survive by support of public at large by maintaining social distancing and following the prescribed guidelines.
Key Words– Pandemic, COVID-19, Lockdown, Impact, Society, International Relation.
INTRODUCTION
Let us understand the word ‘pandemic’ with the basics; a disease is ‘endemic’ if it’s common to a certain area. So, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the amount of a particular disease that’s usually present in a community that’s referred to as the endemic level, when that level spikes up, you get an ‘epidemic’, an outbreak across a region or country or may be even multiple countries. The Ebola outbreak in West Africa 2013 was an epidemic. But, a pandemic that’s when an epidemic goes global. It’s a whole new disease that we don’t really have immunity to fight. It’s crossing borders and continents, spreading quickly from person to person, infecting a large number of people resulting high death toll. Therefore, the word ‘Pandemic’ is said to be a disease prevalent over a whole country or the world. That’s why WHO (World Health Organization) has confirmed COVID-19 to be a ‘pandemic’. The prevailing virus nomenclated as ‘Coronavirus,’ has led to a massive outbreak throughout the globe. The coronavirus has been wreaking havoc throughout the globe since the start of the year. We haven’t experienced a pandemic of this magnitude since the Spanish Flu a century ago.
‘Coronaviruses’ are the family of RNA viruses in the Nidovirales order. This virus is a significant viral pathogens in human and animals causing life threatening disease. The term “Coronavirus” having prefix- ‘Corona’ has been derived from a Latin word for ‘Crown’. It was named for crown like appearances of virus as shown below in Fig. 1.
The virus has four classifications- Alfa, Beta, Gamma and Delta. And human coronaviruses are alpha and beta coronaviruses which we often talk about. These are medium-sized virus that envelops a positive-stranded RNA and they are mostly very large viral RNA genome known.
Hosts, Reservoirs and Infected Animals
- Coronaviruses infect both birds and mammals,
Bats are said to be hosts to the largest number of viral genotypes of coronavirus. So, they don’t necessarily get infected by the virus as their immune system is able to suppress these viruses and just transmit to other birds and mammals. Epidemics can occur when viruses transmit from one species to another which can shockingly acquire mutations in proteins on their envelop that allow viruses to bind the cell and affect other cells more easily. They develop new abilities to infect cells of other species.
- With regards to Humans,
Human-coronaviruses are causes of both respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections. And these viruses are relatively common causes of illness in humans and it’s estimated to account for 5-10 % of all adults’ respiratory tract infections anywhere from “common cold” to pneumonia and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). So, there are wide varieties of signs and symptoms of coronaviruses. Some coronaviruses can even cause GI i.e. gastrointestinal infections symptoms including diarrhoea. So, when mutations occur the virus can be significant causes of epidemics as entirely new species can be developed from it. We have been seeing plethora of cases in the recent past where transmission of one species to another has led to increase the outbreak of the virus thereby enhancing mortality rate. One report demonstrated five cases of 2019-nCoV that appeared to be transmitted by asymptomatic patients.
CORONAVIRUSES: HISTORY OF INFECTIONS
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) – 2002/2003
It seems to be started in Guangdong (Province of China) and is itself a Beta-coronavirus and is said to be in a category of lineage B- Coronavirus. It was believed that this particular coronavirus had been transmitted from bats to civets and all the way to humans. This led to a worldwide outbreak recorded as earliest February 2003 and it seems to have lasted until July 2003. Resources say there were more than 8000 total cases, 774 deaths, fatality rate of approx 9.6%.
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) – 2012
This started in Saudi Arabia and it quickly spread to several countries. It itself is a Beta-coronavirus as well. And what seems to occur here is this virus was said to be transmitted from camels to humans. So, either by eating or exposure or by drinking camel milk they have been infected. Study says more than 2400 cases, 858 deaths, and fatality rate of ~34.4% which is certainly very high.
- 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCOV) – 2019
The newest one which has come on the scene is expected to occur in December, 2019. This occurred in Wuhan, Hubei (Province of China) of more than 11 million people getting affected with “Pneumonia of Unknown Cause”. It was observed that there was an animal market in Wuhan that seems to be an epicentre for this outbreak leading the seventh coronavirus to cause illness in humans. Unlike SARS & MERS it is itself a Novel Beta-coronavirus sharing approximately 80% sequence homology with SARS. Now, a question arises regarding its source of transmission. Some early evidence suggests that it was transmitted from snakes, but more likely from bats to human. As of now human to human transmission is demonstrated in around 210 Countries and Territories around the world having reported a total of 16,525,454 confirmed cases of the coronavirus (COVID-19) and a death toll of 653,970 deaths[3] (till 27th July, 2020). Fig. 2 represents the outline throughout the world. While India reported around 1,479,277 confirmed cases having death toll of around 33,437 cases.[4] Like other coronaviruses, it can cause respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Due to its ability the viral proteins allow binding to respiratory and gastrointestinal cells which can lead to variable respiratory and possible gastrointestinal symptoms. As a result of which World Health Organization had declared a public health emergency on January 30, 2020. The virus has been unstoppably affecting various health care workers and family members of patients. One report demonstrated five cases of 2019-nCoV that appeared to be transmitted by asymptomatic patients. The review in the “Journal of Travel Medicine” was institute that the estimated mean R0 for COVID-19 around 3.28, with a median of 2.79 and IQR of 1.16, which was noticeably higher than the WHO estimation at 1.95[5].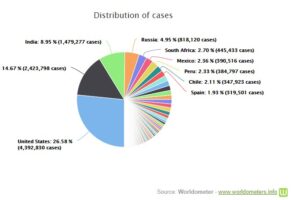
Fig 2: Representation of distribution of cases throughout the world[6] (till 27th July,2020)
IMPACT OF THE PANDEMIC ON INDIAN SOCIETY
The best part of the Indian society is that they have accepted the challenge and are very well aware of the consequences of the non compliance of the guidelines. They have understood the value of life and thereby reaming self quarantine wherever they are had become the last resort to combat with the contamination of the virus. And with such a huge population it is way more difficult to control rather unimaginable without the support of the public at large. It was a very smart step of the government to take such an initiative to announce nation wise lockdown at the early footing of the virus as a result of which in terms of most affected country, India lies at 11th position [7]. Where the highly affected being USA really needs to have a strict implementation of rules to reduce the death toll.
In India when the 1st case was reported in Kerala on 30th January, 2020 and the cases were gradually increasing people were carefree then. However, after an announcement of 14 hour janata curfew on 22nd march, prior to lockdown things started to gets serious after-then as on that day the citizens took part in the curfew by just staying at home. From their balcony, doorways or windows they clapped and rang bells in appreciation for the person delivering essential services. 21 day i.e. (25th March – 14th April) of National lockdown was announced by the Government. On 25th March, the first day of the lockdown, almost all services and factories were pendant[8].
Some of the restrictions were imposed on the citizens such as- People were banned from stepping out of their homes, most of the services and shops were clogged except pharmacies, hospitals, banks, grocery shops and other fundamental services, apart from those commercial and private establishments were shut down and allowed to only work-from-home. For students it might sound fun initially on suspension of all educational, training, research institutions however they were made to join zoom classes and do assignment from home. So that no public gathering may take place all places of worship were closed. All non-essential public and private transport were said to take rest. All sorts of all social, political, sports, entertainment, academic, cultural, religious activities were hanged up.
As a result of which people started to get panic resulting to rush buy of materials from the shop[9], and accordingly many were arrested[10] in violation of the home quarantine. In mean while, isolation wards and quarantine centres started to take their pace to moderate the prevailing situation. To ease the tension for the real warriors who were battling against the pandemic and saving lives of plethora of victims, on 5th April citizens all over India cheered and reflected solidarity with the health workers, police and other fellow worker in that regard by switching off their lights, and lighting candles, flashlight etc. for them for 9 minutes at 9 pm. Positively towards the end of the 1st session of lockdown , the intensification of COVID-19 had considerably declined, from a rate of doubling every three days before lockdown to one of doubling every eight days.[11] However, the lockdown was extended from 15th April to 3rd May as setting free was not a smart choice to be made. Conversely a conditional relaxation was promised after 20th April onwards. After having an empirical approach of the affected areas on 16th April, lockdown areas were classified as “red zone”, representing the presence of infection hotspots, “orange zone” representing some infection, and “green zone” with no infections[12]. After such a long time some relaxation was given to the citizens especially for them lying in green zone. On 25th April, small retail shops were permitted to open with half the staff maintaining social distancing norms.[13] And on 29th April, the Ministry of Home Affairs notified guidelines for the states to permit inter-state movement of the trapped persons like students and tourists far from home[14]. Furthermore, additional extension was announced from 4th May to 17th May in which the Government of India strategically split the country into 3 zones: red zones (130 districts), orange zones (284 districts) and green zones (319 districts)[15].
IMPACT OF THE PANDEMIC: NATIONAL & INTERNATIONAL RELATIONSHIP
It’s unambiguous that now everyone is sharing a common platform, and combating to save the humanity from the pandemic. It has certainly created an adverse impact on the public at large. Various public policies had to be reframed and make viable to the affected community. Public policies shall take account of laws, rules, regulations, judgments, case studies, government programs, etc. And in case of COVID-19 it’s a matter of public safety and Sustenance of livelihood. A chief objective of government is to protect the well-being of its people, most crucially and visibly at the time of emergencies such as the recent outbreak of the coronavirus.
INTERNATIONAL PERSPECTIVE
At International level also the battle is on active mode and on a global platform all are co-ordinating with each other to come out from this grave situation. So, be it formation of H1 drug i.e. hydroxychloroquine or PPE kit, all are disseminated keeping a paramount consideration to save the human race. Certainly, this is not the time to play game of politics so all are optimistically to taking it on a serious note. Positively the International Monetary Fund has $50 billion available in rapid-disbursing emergency financing to help countries suffering from the virus. Not only that the IMF has announced immediate debt relief for 25 poor countries to help them free up funds to fight the coronavirus pandemic. Subsequently, the World Bank announced that it would roll out USD 160 billion in emergency aids over 15 months to help countries suffering by the virus, including USD 14 billion in debt repayments from 76 deprived countries to other governments[16]. As a trans-boundary crisis, COVID-19 reflects a paramount challenge to public leaders and their policy advisors, who are likely to perform key functions like taking decisive action, handling overwhelming amounts of data, constructing critical decisions regarding resource allocations, and coordinating with stakeholders. WHO COVID-19 Incident Management Team is functioning personally with partners across all levels to provide sustenance to countries, fortify technical and operational networking and collaboration, and support operational coordination of the global response.
NATIONAL PERSPECTIVE
Approach of Indian Government : Indian government has affirmatively launched various policies and programs with help of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to slow down the spread of the virus, as a result of which the situation has not become worst yet.
Three intersecting sets of legal regimes.
First, at the central level, the government has invoked the National Disaster Management Act, 2005[18]. Section 10 of the NDMA authorizes the central authority to issue guidelines and directions to the several state governments with respect to addressing disasters. The Authority’s Guidelines[19] issued on 24th March 2020, and supplemented by various addenda from time to time – required a closure of government offices, commercial establishments, (with certain exceptions), industrial establishments, transport services, hospitality services, places of worship, large gatherings, and so on.
Secondly, several state governments have invoked the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897[20] a legislation that grants to the states formally unlimited powers to prevent the outbreak or spread of an epidemic.
These Regulations intersect more closely with the third legal regime, which separates Section 144[21] orders passed by individual magistrates/Commissioners of Police.
Apart from that Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has maintained transparency in resources at the time of outbreak. Some of its cogent steps are-
- Advisory against spraying of disinfectant on people for COVID-19 management[22].
- Central Medical Services Society[23].
- Revised Guidelines for Dialysis of COVID-19 Patients[24].
- Ayurveda’s immunity boosting measures for self care during COVID 19 crisis[25].
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package: Insurance Scheme for Health Workers Fighting COVID-19[26].
- Guidelines for Quarantine facilities[27].
- Guidelines for Handling, Treatment and Disposal of Waste Generated during Treatment/Diagnosis/ Quarantine of COVID-19 Patients[28].
- Gazette Notification – Hydroxychloroquine now a schedule H1 drug, can be sold on prescription only[29].
Moreover, through a video conference on March 25, leaders of the world’s major economies (G-20) stated that they were devoted to restore confidence, preserve financial stability and revive growth. They said they were firm to resolve disruptions to global supply chains and pleaded finance ministers and central banks to synchronize regularly with international organizations to widen an action plan in response to the pandemic[30].
SUGGESTIONS
Some of the paramount steps government should entertain to fight against the pandemic-
Firstly effective communication, can act as a main pillar of crisis governance.
Secondly, adopting a whole-of-society approach shall be significant in this crisis.
Finally, implementing evidence-based strategies dependent on historical in addition to current data is vital.
Fig. 3 Illustration of Whole-Of-Society Approach
The diagram above in Fig. 3 depicts the whole-of-society approach[17]. It is illustrated by the three circles in the central point of the diagram: government, civil society, and business. The pyramids within each of the circles correspond to the levels within each sector (including sub national, local government, and community). The nine circles in the region of the disaster management continuum of readiness, response, and recovery symbolize nine key essential services).
CONCLUSION
We all are well aware of the fact that there is no straight jacket formula to swing the magic wand and cure the pandemic all of a sudden. There can be no ideal solution to the same still research experiments are going on by our scientists throughout the world. We know the impact of the virus is getting worst day by day. And in context to India empirical approach suggests that if the statistics continue to show a relatively low infection rate, then India will have helped lead the way in containing coronavirus. And the same rule applies throughout the world. We all just need to have the situational awareness through dissemination of basic information. All together we can reduce the pandemic spread by curtailing interactions with the symptomatic patient moreover help in diminishing susceptibility towards public at large. Above all some things cannot be ignored that this is the high time we must understand that nature is retaliating in its worst form. And we all are given time to collect our shit together and understand the meaning of sustainability. And I am quite sure that we shall stand strong and develop physical as well as mental immunity to combat from any such unprecedented pandemic. However, this lock-down has certainly gives everyone a space to realize his potential in various facets. Lastly, we all pray the Almighty to help us to come out from this pandemic and ease the state of affairs as soon as possible.
[1] AUTHOR- JHA PRANAV KUMAR, STUDENT, B.A.LL.B 4TH YEAR, DEPT. OF LAW, ALIGARH MUSLIM UNIVERSITY, CENTRE MURSHIDABAD, WEST BENGAL
[2] Source- ALISSA ECKERT, DAN HIGGINS/CDC https://www.statnews.com/2020/02/11/disease-caused-by-the-novel-coronavirus-has-name-covid-19/ viewed on 26th April,2020
[3] https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/countries-where-coronavirus-has-spread/ viewed on 15th May,2020
[4] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/ viewed on 15th May,2020
[5] Journal of Travel Medicine, Volume 27, Issue 2, March 2020, taaa021, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taaa021 viewed on 28th April, 2020
[6] https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/ viewed on 15th May, 2020
[7] https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ viewed on 16th May
[8] Singh, Karan Deep; Goel, Vindu; Kumar, Hari; Gettleman, Jeffrey (25 March 2020). “India, Day 1: World’s Largest Coronavirus Lockdown Begins”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331.
[9] Covid-19: People flock to wholesale markets in UP, West Bengal amid lockdown, ANI, 24 March 2020
[10] Day 1 of coronavirus lockdown: India registers 101 new cases, 3 deaths; Govt says working to deliver essential services”. India Today
[11] Gupta, Shekhar (18 April 2020). “Covid hasn’t gone viral in India yet, but some in the world & at home can’t accept the truth”. ThePrint. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
[12]India coronavirus: All major cities named Covid-19 ‘red zone’ hotspots”. BBC. 16 April 2020.
[13] Aleem, Zeeshan (25 April 2020). “India takes a small step toward relaxing its strict lockdown”. Vox.
[14] MHA allows movement of migrants, tourists, students stranded at various places”. Livemint. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020
[15] Thacker, Teena (1 May 2020). “Centre issues state-wise division of Covid-19 red, orange & green zones”. The Economic Times
[16] https://www.indiatoday.in/world/story/coronavirus-pandemic-imf-approves-debt-relief-for-25-poor-countries-1666865-2020-04-14 viewed on 29th April, 2020
[17] https://www.who.int/influenza/preparedness/pandemic/2009-0808_wos_pandemic_readiness_final.pdf viewed on 29th April, 2020
[18] https://ndma.gov.in/images/covid/MHAorder240320.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[19] https://ndma.gov.in/images/covid/Guidelines.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[20] https://indiacode.nic.in/bitstream/123456789/10469/1/the_epidemic_diseases_act%2C_1897.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[21] https://twitter.com/TheLeaflet_in/status/1241681267633967105/photo/1 viewed on 28th April, 2020
[22]https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/AdvisoryagainstsprayingofdisinfectantonpeopleforCOVID19managementFinal.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[23] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/MedicalOxygenCylinder.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[24] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/RevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[25] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ImmunityBoostingAYUSHAdvisory.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[26]https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/FAQPradhanMantriGaribKalyanPackageInsuranceSchemeforHealthWorkersFightingCOVID19.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[27] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/90542653311584546120quartineguidelines.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[28] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/63948609501585568987wastesguidelines.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[29] https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/218927g.pdf viewed on 28th April, 2020
[30]https://tribune.com.pk/story/2186955/6-public-policy-pandemic/ viewed on 28th April, 2020




