HUMAN RIGHTS VIOLATIONS

India, the world’s largest democracy, has had a long-standing history of human rights violations. Despite being a signatory to various international human rights treaties, the country has struggled to provide basic human rights to its citizens. Here are some of the major human rights violations in India:
Extrajudicial Killings: Extrajudicial killings, also known as fake encounters, are a major human rights violation in India. Police and security forces have been accused of staging fake encounters to kill alleged criminals, terrorists, or insurgents. These extrajudicial killings often involve the use of excessive force, torture, and other forms of brutality.

Police Brutality: Police brutality is another serious human rights issue in India. Police officers have been accused of using excessive force, torture, and other forms of brutality while dealing with suspects and detainees. Police brutality often goes unpunished, and victims are often denied justice.
Torture: Torture is a widespread practice in India, particularly in police custody. Detainees are often subjected to physical and psychological torture to extract confessions or information. Torture is also used as a form of punishment or retaliation.

Discrimination: Discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, and ethnicity is a major human rights issue in India. Dalits, or people from lower castes, face discrimination and violence on a daily basis. Minorities, such as Muslims and Christians, also face discrimination and violence.
Violence Against Women: Violence against women, including rape, sexual assault, and domestic violence, is a major human rights issue in India. Women are often blamed for the violence they face and are discouraged from reporting it. The justice system is often slow to respond, and perpetrators are rarely punished.
Child Labor: Child labor is a serious human rights violation in India. Millions of children are forced to work in hazardous conditions, often for very little pay. Child labor deprives children of their childhood and their right to education.
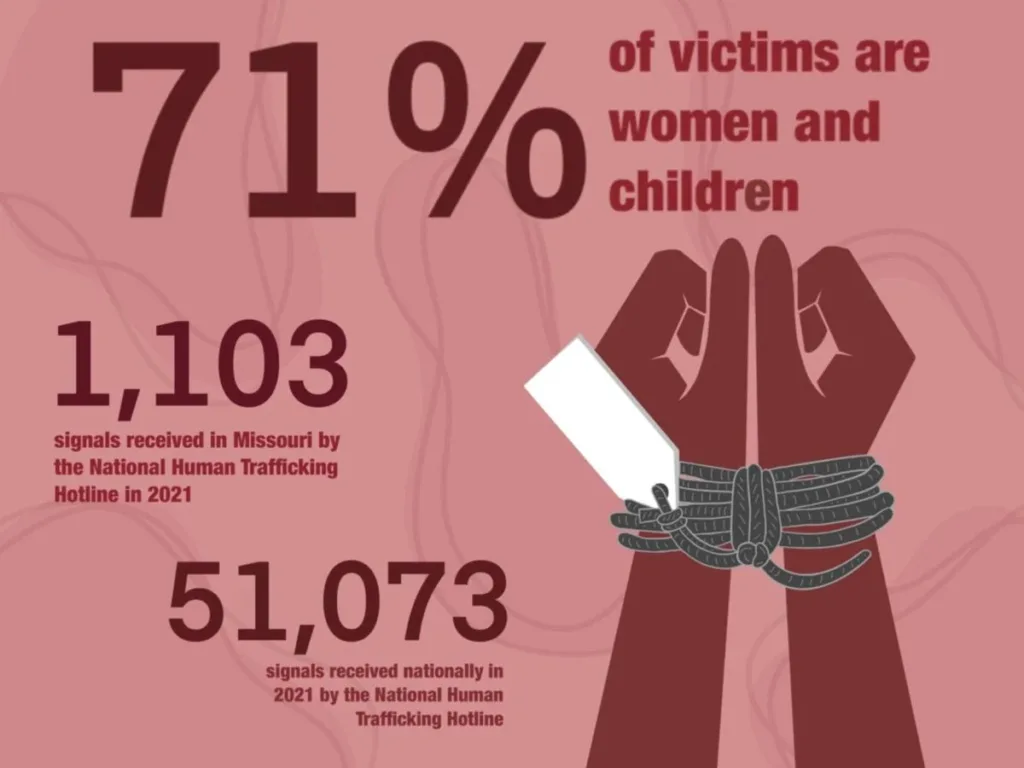
Human Trafficking: Human trafficking is a major human rights issue in India. Women and children are often trafficked for sexual exploitation or forced labor. The government has taken steps to combat human trafficking, but the problem persists.
Religious Violence: Religious violence is a major human rights issue in India. Communal clashes between Hindus and Muslims have resulted in the deaths of thousands of people over the years. The government has been criticized for failing to prevent these clashes and for not prosecuting those responsible.
Freedom of Expression: Freedom of expression is often restricted in India. Journalists, activists, and other critics of the government are often harassed, intimidated, and arrested. Social media platforms have also faced pressure to censor content critical of the government.
Kashmir Conflict: The conflict in Kashmir, a region disputed between India and Pakistan, has resulted in human rights violations by both countries. The Indian government has been accused of using excessive force, torture, and other forms of brutality against Kashmiri civilians. The conflict has resulted in the displacement of thousands of people and has had a severe impact on their human rights.

In conclusion, India faces a range of human rights issues, including extrajudicial killings, police brutality, discrimination, violence against women, child labor, human trafficking, religious violence, restrictions on freedom of expression, and the Kashmir conflict. While the government has taken steps to address some of these issues, more needs to be done to protect the human rights of all citizens.
India has had a history of human rights violations, some of which have been addressed through case law. Here are some examples:
Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India (1978) – This landmark case expanded the scope of Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, which guarantees the right to life and personal liberty, to include the right to travel abroad. It was a significant victory for human rights in India.
People’s Union for Democratic Rights v. Union of India (1982) – In this case, the Supreme Court of India held that bonded labor, a practice where a person is forced to work to pay off a debt, violates the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution.
Rudul Shah v. State of Bihar (1983) – This case established that custodial torture is a violation of the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
Vishaka v. State of Rajasthan (1997) – This case addressed sexual harassment of women in the workplace and established guidelines to prevent it. The guidelines, known as the Vishaka Guidelines, are considered a landmark in the fight for gender equality and women’s rights in India.







