India's Extrajudicial Killings Concerns

Extra-judicial killings, also known as extrajudicial executions, refer to the killing of individuals by state actors or individuals acting on behalf of the state, outside the legal framework or without due process of law. In India, there have been concerns and reports of extrajudicial killings, which raise human rights issues.
Human rights are fundamental rights and freedoms that are inherent to all individuals, regardless of their nationality, ethnicity, religion, or any other status. They include the right to life, liberty, and security of person, the right to a fair trial, and the prohibition of torture, among others.
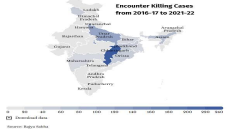
In India, there have been reported cases of extrajudicial killings, particularly in the context of encounters between law enforcement agencies and alleged criminals, terrorists, or militants. These encounters often involve the use of lethal force by the police or security forces, resulting in the death of the alleged suspects, without following proper legal procedures, such as arrest, investigation, and trial.
Such extrajudicial killings have been criticized for violating the right to life and due process of law, as enshrined in the Indian Constitution and international human rights standards, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Extrajudicial killings and concerns:
One of the main concerns in extrajudicial killings in India is the lack of accountability and impunity for the perpetrators. There have been allegations of fake encounters, where suspects are allegedly killed in staged encounters to avoid legal procedures or accountability.
Human rights organizations have raised concerns about the lack of independent and transparent investigations into such cases, and the need for holding perpetrators accountable through fair and impartial judicial processes.
There have been efforts by human rights organizations and civil society in India to raise awareness about extrajudicial killings and advocate for accountability and justice for the victims. There have also been legal challenges and interventions by the judiciary to address this issue, including directives to investigate and prosecute cases of extrajudicial killings.
However, more needs to be done to ensure that human rights are respected and protected, and that extrajudicial killings are thoroughly investigated and those responsible are held accountable in accordance with the rule of law and international human rights standards.
Marginalized more prone to encounters:
Additionally, it’s important to note that extrajudicial killings often disproportionately affect marginalized and vulnerable communities in India, such as religious and ethnic minorities, indigenous peoples, and economically disadvantaged individuals.
There have been reports of extrajudicial killings targeting individuals based on their perceived identity or affiliation, without proper evidence or legal procedures, which raises concerns of discrimination and violation of human rights, including the right to non-discrimination and equality.
The use of excessive force and extrajudicial killings by law enforcement agencies may also contribute to a culture of impunity, where state actors feel empowered to act outside the legal framework and disregard human rights. This can erode trust between communities and law enforcement agencies, and undermine the rule of law, leading to a breakdown of the justice system and hindering access to justice for victims and their families.
India is a party to various international human rights treaties, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (CAT), which prohibit extrajudicial killings and torture.
As such, India has an obligation to ensure that its law enforcement agencies operate in compliance with these international human rights standards, and that victims of extrajudicial killings have access to effective remedies, including impartial investigations and fair trials.

Addressing the issue of extrajudicial killings:
To address the issue of extrajudicial killings and uphold human rights in India, it is important for the government to take concrete measures, such as:
(1)Ensuring thorough, prompt, and impartial investigations into all allegations of extrajudicial killings, with accountability for perpetrators, regardless of their rank or status.
(2)Strengthening the oversight mechanisms of law enforcement agencies to prevent and address extrajudicial killings, including independent and transparent civilian oversight bodies.
(3)Promoting and protecting the rights of marginalized and vulnerable communities, and addressing any discrimination or bias in law enforcement practices.
(4)Enhancing human rights training and education for law enforcement personnel, to promote a culture of respect for human rights and the rule of law.
(5)Ensuring access to justice and reparations for victims of extrajudicial killings and their families, including compensation, rehabilitation, and support.
(6)Engaging with civil society organizations and human rights defenders to promote dialogue and collaboration in addressing the issue of extrajudicial killings and human rights in India.
It is also crucial to address the underlying factors that may contribute to extrajudicial killings, such as systemic issues within law enforcement agencies, lack of training, inadequate resources, and pressures to achieve high arrest or conviction rates.
Reforms within law enforcement agencies, including improving their capacity, training, and adherence to human rights standards, can help prevent extrajudicial killings and promote a culture of respect for human rights.

Additionally, promoting transparency and accountability in the handling of encounters and use of force by law enforcement agencies is important.
This includes ensuring that there are robust mechanisms for monitoring and oversight, including independent investigations, and holding perpetrators accountable through fair and impartial judicial processes. It also requires protecting whistleblowers and witnesses who come forward to report incidents of extrajudicial killings.
Civil society organizations, human rights defenders, and the media play a crucial role in raising awareness, monitoring, and advocating for human rights, including the issue of extrajudicial killings. It is important to create an enabling environment for their work, ensuring that they can operate freely, without fear of reprisals or harassment.
Lastly, it is important for the Indian government to engage in dialogue and cooperation with international human rights bodies, such as the United Nations and its human rights mechanisms, and other international stakeholders, to address the issue of extrajudicial killings and human rights concerns in India. International scrutiny and accountability can provide additional leverage in promoting human rights and addressing extrajudicial killings.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, extrajudicial killings in India raise significant human rights concerns, including the right to life, due process, non-discrimination, and accountability. It is essential for the Indian government to take effective measures to prevent and address extrajudicial killings, uphold human rights, and ensure justice for the victims and their families.
Promoting a culture of respect for human rights and the rule of law, strengthening accountability mechanisms, and promoting dialogue and collaboration with civil society organizations are critical steps towards addressing this issue and protecting human rights in India.
Furthermore, it is important to ensure that victims of extrajudicial killings and their families have access to effective remedies and redress mechanisms. This includes impartial and independent investigations into alleged extrajudicial killings, fair and transparent trials, and appropriate compensation and rehabilitation for victims and their families.
Addressing the issue of extrajudicial killings and upholding human rights in India requires comprehensive efforts, including legal reforms, strengthening accountability mechanisms, promoting transparency, engaging with civil society, and addressing underlying systemic issues.
Protecting the right to life, due process, non-discrimination, and accountability are fundamental principles that must be upheld to ensure that human rights are respected and protected for all individuals in India.







