Human Trafficking Crisis
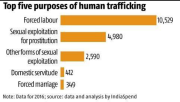
Millions of people around the world are impacted by human trafficking, which is a complicated and widespread problem. It entails the exploitation of weak people who are coerced or forced into prostitution, forced labour in the mining, agriculture, and construction industries, as well as domestic servitude and forced labour.
A serious violation of human rights, human trafficking is a situation that requires our attention and response.
People of all ages, genders, and origins are affected by the enormous extent of human trafficking. Human trafficking especially affects women and children, with women and girls making up about 71% of the victims. Around 29% of victims of trafficking are men, making men another vulnerable demographic.
One of the nations in the world with the greatest number of victims of human trafficking is India. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reports that there were 8,132 victims in 5,466 reported cases of human trafficking in India in 2018. However, due to the fact that many cases go undetected, experts think that the true number of cases of trafficking is far greater.
In India, women and children are particularly at risk from trafficking. Women made up 60% of all trafficking victims in 2018, while children made up 23%, according to the NCRB. Additionally, girls make up about 40% of the youngsters who are trafficked in India. Many of these victims fall for deceptive marriage or employment proposals, which forces them into prostitution or other forms of forced labour.

The rights to work and be paid fairly, to live in freedom and security, to travel around freely, to acquire an education, and to have good health are just a few of the fundamental rights that are violated by human trafficking. The majority of trafficking victims experience physical and psychological abuse, are made to work in denied access to medical treatment and education, as well as unsafe and demeaning conditions.
Human trafficking has numerous, interconnected primary causes. Some of the reasons that increase a person’s vulnerability to human trafficking include poverty, a lack of access to education and work prospects, social and political unrest, and gender-based discrimination. In addition, the expansion of globalisation and the rising need for inexpensive labour have fostered a climate conducive to human trafficking.
In order to combat human trafficking, governments, international organisations, and civil society organisations have taken a number of actions, such as creating legislative frameworks, offering victim support services, and putting preventative programmes into action. To combat this situation, additional work must be done.
The lack of knowledge and comprehension of the problem of human trafficking is one of the major obstacles to its prevention. There is a need for further education and awareness-raising initiatives because many individuals are ignorant of the extent and gravity of human trafficking. In order to combat the transnational aspect of this crime, there is also a need for improved international collaboration, stronger enforcement of human trafficking laws and regulations, and other relevant measures.
Additionally, it is essential to deal with the source by giving disadvantaged people and communities more economic and social opportunities. causes of human trafficking. This includes initiatives to combat gender-based inequality and discrimination, as well as initiatives to lessen poverty and provide access to healthcare and education. India has a high frequency of trafficking due to a number of variables, including its large population, poverty, and gender inequity.
Women and children are more susceptible to exploitation because they lack access to education and work possibilities, especially in rural areas. Further, the absence of legal protection for sex workers and the societal shame attached to prostitution renders them vulnerable to trafficking.
Human trafficking still exists despite attempts by the Indian government and civil society organisations to stop it. A comprehensive legal framework to fight trafficking is intended by the Trafficking of Persons (Prevention, Protection and Rehabilitation) Bill, which was passed in 2018. However, it has drawn criticism for placing too much emphasis on law enforcement and not enough on victim care assistance and protection.
In order to effectively combat trafficking in India, prevention efforts must be prioritised. These initiatives should include programmes for vulnerable populations’ economic and social empowerment as well as education and awareness-raising activities. Additionally, more needs to be done to safeguard and aid victims of trafficking, including giving them access to legal, educational, and medical help.
A multifaceted strategy encompassing prevention, protection, legal action, and collaboration is needed to address the human trafficking epidemic in India. The following are some tactics to combat human trafficking in India:
1. Legislation and Law Enforcement: Strengthen and enforce current anti-human trafficking laws, such as the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act and the Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act (ITPA). bolster the ability of law enforcement organisations to find, look into, and convict traffickers.
2. Victim Identification and Support: Specifically among vulnerable populations like women and children, improve victim identification techniques. Create shelters and safe houses that offer survivors of trafficking a full range of support services, such as medical attention, counselling, legal assistance, and skill development.
3. Education and Awareness: Launch extensive education and awareness campaigns to inform communities, at-risk populations, and front-line personnel about the dangers of human trafficking. Create awareness campaigns in communities, colleges, and schools to encourage people to spot and report cases of human trafficking.
4. Strengthening Border Control: To stop cross-border trafficking, improve border security and cooperation between law enforcement authorities. Especially in high-risk locations, implement strict screening processes at entry and departure points.
5. Economic Empowerment: Encourage livelihood and skill-development initiatives to give at-risk people, especially women and girls, the opportunity to earn money and marketable skills. This can lessen their susceptibility to traffickers who take advantage of their financial situation.
6. Demand Reduction: Fight the demand for trafficked people by launching public awareness campaigns on the negative effects of participating in trafficking and buying trafficked people. Implement severe sanctions for traffickers and step up your efforts to take down organised trafficking networks.
7. International Cooperation: To combat cross-border trafficking, and enhance collaboration with international organisations, neighbouring nations, and law enforcement agencies. To dismantle international trafficking networks, exchange knowledge, intelligence, and best practices.
8. NGOs and Civil Society Empowerment Support and resources should be made available to civil society and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) engaged in anti-trafficking campaigns. Promote collaborations between government organisations, non-governmental organisations, and community-based groups to improve the efficacy of prevention and rehabilitation activities.
9. Victim-Centered Approach: Adopt a victim-centred strategy that places emphasis on the rights, safety, and well-being of survivors. Ensure they are involved in decision-making, give them access to justice, and shield them against future trafficking.
10. Data gathering and Research: To better comprehend the trends, patterns, and underlying causes of human trafficking in India, increase data gathering and research initiatives. This can help guide the allocation of resources and evidence-based policies.
All interested parties, including the government, civil society, law enforcement organisations, communities, and people, must maintain a persistent commitment to combating human trafficking. India can fight to prevent trafficking, protect victims, and bring perpetrators to justice by putting these strategies into practice and encouraging cooperation, thereby lowering the frequency of this horrible crime.
In conclusion, the situation of human trafficking necessitates an immediate response, especially for women and children. It is a major violation of human rights. A multi-pronged strategy is needed to address this issue, including initiatives to deal with the underlying causes of trafficking, offer assistance to victims, and strengthen legal frameworks to deter trafficking and hold offenders accountable. Together, we can build a society in which no person is in danger of exploitation or oppression.







