Breaking the Silence: Addressing Reproductive Rights of Women in Rural India

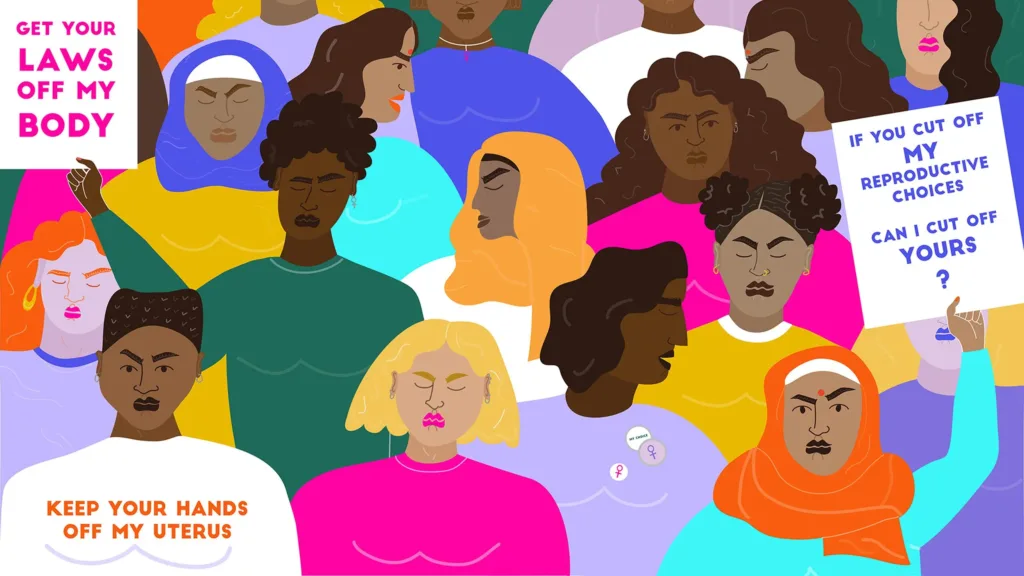
Reproductive rights are the basic human rights of all individuals to have control over their reproductive health, including access to safe and legal abortion, family planning services, and healthcare. Unfortunately, women in rural India face significant challenges in accessing these rights, including limited access to healthcare facilities, lack of awareness and education, and social stigmas.
In this article, we will explore the barriers that rural women in India face in accessing reproductive rights and suggest some solutions to address these issues. In India, social norms and traditions are still deeply patriarchal, which has resulted in the marginalization of women’s reproductive rights. For instance, the pressure on women to have male children is intense, and women who cannot produce male heirs may face discrimination or even violence.

Additionally, women are often denied access to reproductive healthcare services due to the stigma associated with contraception and abortion. Men also dominate decision-making processes regarding family planning, often without considering women’s preferences or needs.
Barriers to Reproductive Rights in Rural India-
- Limited Access to Healthcare Facilities
In rural India, healthcare facilities are often scarce, and women often have to travel long distances to access healthcare services. This can be a significant barrier for women who need reproductive healthcare services, such as family planning, prenatal care, or abortion. Moreover, healthcare facilities in rural areas are often understaffed and lack the necessary equipment and supplies to provide quality care. - Lack of Awareness and Education
Many women in rural India are not aware of their reproductive rights and the available healthcare services. Women often lack the knowledge and understanding of their bodies, including basic menstrual hygiene. This lack of awareness and education can lead to unintended pregnancies, unsafe abortions, and other reproductive health issues. - Social Stigmas and Norms
Social stigmas and norms in rural India often discourage women from seeking reproductive healthcare services. Women who seek abortions or use contraceptives are often stigmatized and ostracized by their communities. Moreover, many women are subject to gender-based violence, which can further limit their ability to access reproductive healthcare services.
Solutions to Address Reproductive Rights in Rural India - Improving Healthcare Facilities
To address the limited access to healthcare facilities in rural India, the government and NGOs need to invest in improving healthcare infrastructure. This includes increasing the number of healthcare facilities and staff in rural areas and providing necessary equipment and supplies. Moreover, telemedicine and mobile health units can also be utilized to provide access to healthcare services in remote areas. - Increasing Awareness and Education
To address the lack of awareness and education, the government and NGOs can implement educational programs on reproductive health and rights. This includes educating women on menstrual hygiene, family planning, and safe sex practices. Moreover, community health workers can be trained to provide information and support to women in rural areas. - Challenging Social Stigmas and Norms
To address the social stigmas and norms, the government and NGOs need to engage in advocacy and awareness-raising campaigns. These campaigns should challenge the stereotypes and misconceptions surrounding reproductive health and rights. Moreover, community-based interventions can be implemented to promote gender equality and combat gender-based violence.

Conclusion
Reproductive rights are essential human rights that should be accessible to all individuals, regardless of their geographic location or socio-economic status. Women in rural India face significant barriers in accessing these rights, including limited access to healthcare facilities, lack of awareness and education, and social stigmas.
To address these issues, the government and NGOs need to invest in improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing awareness and education, and challenging social stigmas and norms. By breaking the silence surrounding reproductive rights in rural India, we can ensure that all women have access to the healthcare services they need to make informed decisions about their bodies and their lives.
To address the challenges faced by rural women in accessing reproductive healthcare, community-based solutions are essential. This approach involves engaging with local communities to raise awareness and build support for women’s reproductive rights.
Community health workers can play a crucial role in providing information and support to women, particularly in areas where access to healthcare is limited. Involving men in these initiatives can also help to shift gender norms and promote more equitable decision-making processes. Ultimately, community-based solutions can empower women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health, leading to better health outcomes and greater gender equality